Environmental Factors
A recent study investigated a potential link between the microorganisms in the gut and the symptoms of neurodevelopment disorders like Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Explore this page to learn about some of the non-genetic factors already linked to ASD.

Key Questions
What evidence supports a role for the environment in autism?
What parental factors are associated with autism?
What drugs are associated with autism?
What is the role of diet in autism?
What pesticides and heavy metals are associated with autism?
• Over the past twenty years autism rates have risen by over 600%. The Centers for Disease Control now estimates an autism prevalence of 1:88 individuals (as of April, 2012). Social factors alone cannot explain this dramatic increase. In fact, changes in diagnostic criteria and increased awareness could account forsome of the increase in autism prevalence. However, increasing evidence suggests a role for environmental factors and individual genetic vulnerabilities in the etiology of autism.
• The environmental causes of autism are fiercely debated and extremely controversial. With the exception of a few seldom-used teratogenic drugs, specific environmental factors are linked to autism by association, not causation, and few such factors have been rigorously tested. However, there is compelling evidence that environmental exposures can contribute to neurodevelopmental disorders (i.e. alcohol and lead). Accordingly, the scientific literature has associated numerous environmental factors with autism and broader Autism Spectrum Disorders. Currently, environmental factors as diverse as parental factors, obstetric complications, vitamin deficiencies, exposures to drugs and environmental contaminants, immune challenge, and socio-economic status have been implicated in the increased prevalence of autism / ASD.
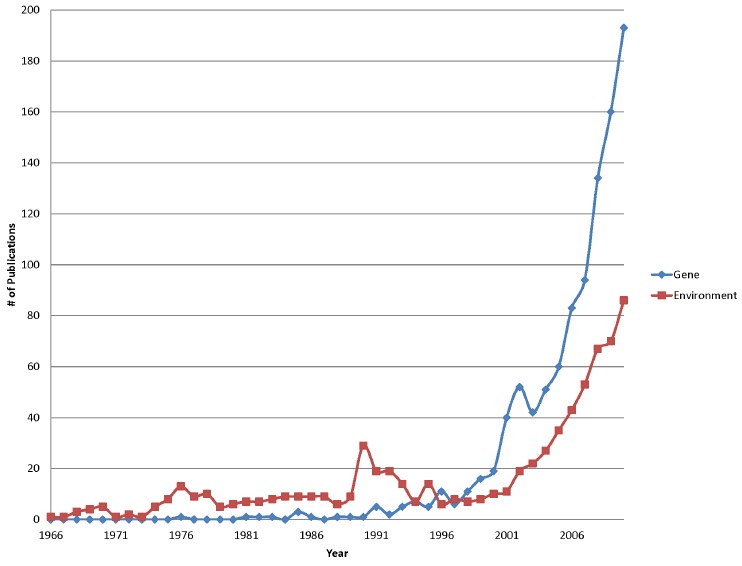
Distribution of the number of publications referencing “Autism and genes” and “Autism and environment” in the PubMed Database from 1973-2010.
• For decades the scientific community has largely focused on the genetic basis of autism. However, the findings of a recent innovative study of autism/ASD concordance rates in identical versus fraternal twins[What Evidence Supports a Role for the Environment in Autism?] challenge the dogma that autism is solely a genetic disorder, instead suggesting that environmental factors contribute substantially to autism liability. It is unlikely that autism is caused by exposure to a single environmental factor. Instead, it may be caused by the complex interaction between individual genetic susceptibilities and environmental factors.
Key Points
- An environmental factor is any factor that influences us.
- New research supports a role for the environment in autism.
- Numerous environmental factors have been associated with increased autism risk.
Misconception
The measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine causes autism.
Fact
The original study that reported a correlation between MMR vaccination and autism has been retracted and repudiated by the scientific community. Studies conducted by researchers in the United States, United Kingdom, Europe, and Japan have failed to establish any causative link between vaccinations and autism. Unfortunately, although the vaccine–autism link has been widely discredited, the dangerous misconception that vaccines cause autism persists in the face of no sound scientific evidence.
Read about other misconceptions.

