Check out other stories from the Latest News
Link Found Between Neural Stem Cell Division and Autism
By Shana R. Spindler, Ph.D. on March 2, 2016
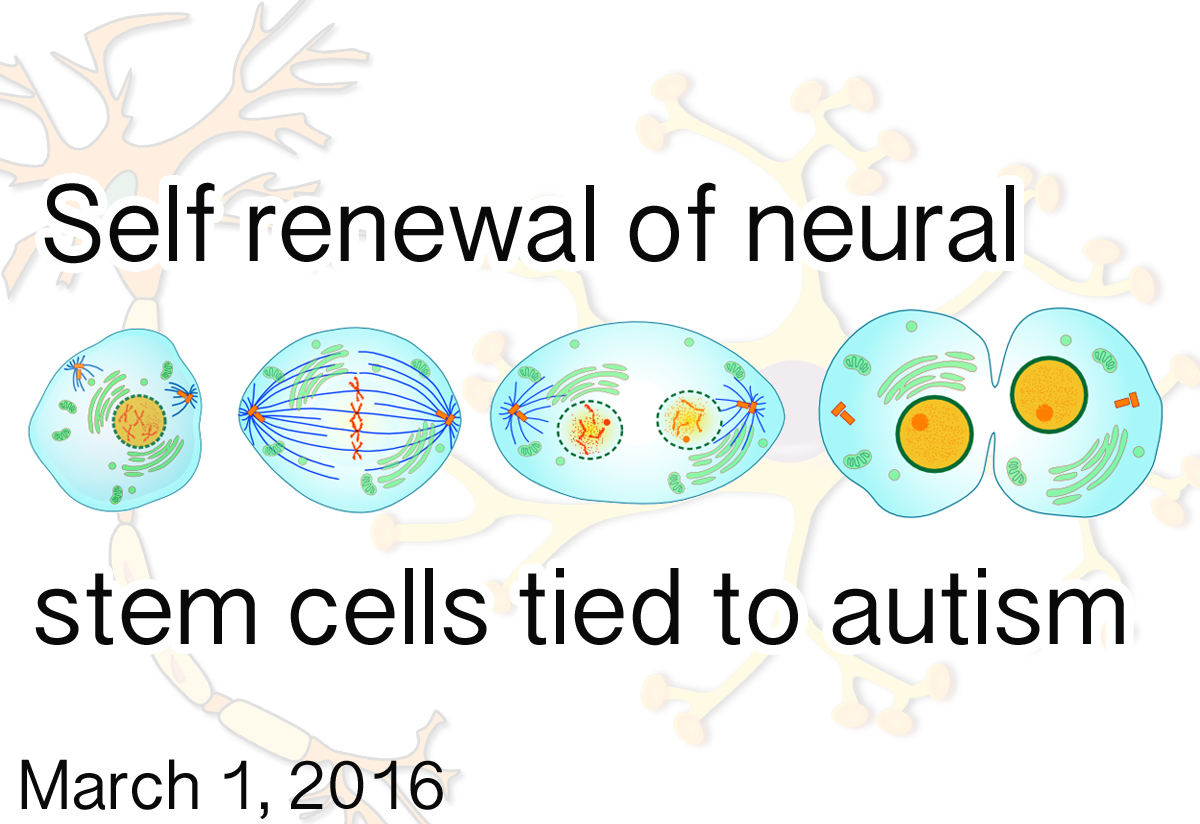
Background: The brain grows, in part, through the activity of neural stem cells—a cell population that replenishes itself through cell division. When a stem cell divides, it has three choices. It can make two new stem cells, a stem cell and a new cell type (such as a neuron), or two new cell types.
What’s new: An error in neural stem cell division may be at the root of neurodevelopmental problems seen in some metabolic disorders, according to a new study published February 9, 2016, in Cell Reports. Researchers used mice to study if neural stem cell division requires the autism risk gene TMLHE—which is an important contributor to metabolism and energy production in the powerhouse of the cell.
They found that TMLHE is required to maintain the proper balance between neural stem cell self-renewal versus the production of different cell types. The researchers showed that providing TMLHE-deficient stem cells with carnitine, a normal product of TMLHE activity, restored the balance of neural stem cell divisions.
Why it’s important: This study provides a potential mechanism for how a known autism risk gene leads to a type of autism associated with a metabolic disorder. Most importantly, the findings suggest an avenue for treating the disorder during embryonic development with carnitine, a common nutritional supplement. While it may be tempting to get excited, this is a far off goal, as many—many—additional studies are needed before attempting to study this in humans.
Help me understand :
| Source(s) : |
| Tweet |

