Check out other stories from the Latest News
Strong Evidence for a Genetic Link to Autism
By Sharmila Banerjee-Basu, Ph.D. on July 10, 2014
Background: The genetic landscape of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is complex. Diverse types of DNA variation—from rare mutations with large effects to common variations with small effects—are thought to contribute to the development of the disorder. Many autism-associated mutations are known, but how each one contributes to autism is not well established.
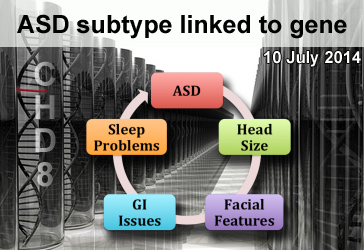
What’s new: A new study published online in the scientific journal Cell shows convincing evidence that the gene CHD8 is linked to a subtype of autism. Researchers identified eight new CHD8 mutations in 3,730 individuals with developmental delay or ASD. In contrast, the team failed to find similar CHD8 mutations in 8,792 control individuals. Including ASD individuals carrying CHD8 mutations from previous studies, the researchers further examined detailed clinical characteristics in a total of 15 individuals with CHD8 mutations. In addition to ASD, CHD8 mutation carriers have many common features, including significantly increased head size, distinct facial features, gastrointestinal (GI) issues, and sleep problems.
Why it’s important: With rapid advances in genomic technologies, a field of study is emerging where sub-types of autism can be recognized based on mutations in specific genes. Importantly, 13 out of 15 individuals with CHD8 mutations in this study had a diagnosis of ASD, indicating a strong link between CHD8 disruption and ASD onset. One can hope that genetic testing may aid in the diagnosis and treatment decision making in autism in the near future.
Help me understand :
| Source(s) : |
| Tweet |

